Hello Friends,
Its been long time i did not put any contents in my blog. I was doing research in some interesting stuffs in linux and also busy with work. This time i am coming up with SuSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 not with Redhat. !
Let us discuss about how do we configure PXE server to install SuSE Linux Enterprise server OS into Clients. Similar post on RHEL 7 can be found on the following link : Complete Guide for PXE Server configuration in RHEL 7.0
Breaking down the task to configure PXE Server, Here is the list :
1. DHCP server ( To provide IP address to client )
2. Apache2 Server configuration ( To transfer the DVD image to Client for OS installation)
3. TFTP server configuration ( To Transfer the PXE kernel and other supporting files to Client System )
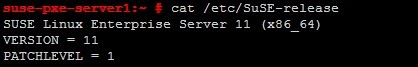
Check the version of SUSE Linux using the following command.
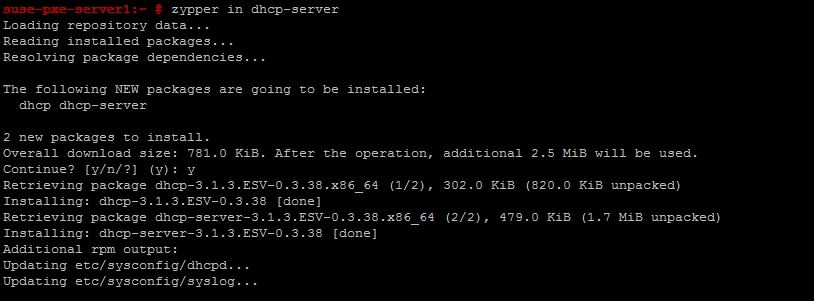
Let us configure DHCP Server first. for that we need to install the dhcp-server package into server.
I am using Zypper to install dhcp server pakage. or else you could run #yast dhcp-server to install and configure dhcp server.
# zypper in dhcp-server
Now configure dhcp server. edit the /etc/dhcpd.conf and update the following entries.
(Move original /etc/dhcpd.conf file to some other name and create new dhcpd.conf with the following entries.)
Here IP range is from 192.168.1.10 to 192.168.1.20
default-lease-time 14400;
ddns-update-style none;
subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range dynamic-bootp 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.20;
default-lease-time 14400;
max-lease-time 172800;
next-server 192.168.1.3;
filename "pxelinux.0";
}
update the /etc/sysconfig/dhcpd file with the following entries.
DHCPD_INTERFACE="eth0"
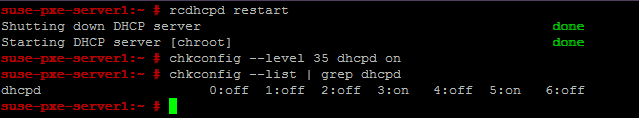
Restart the dhcpd service and enable it on start-up using the following command.
# rcdhcpd restart
#chkconfig --level 35 dhcpd on
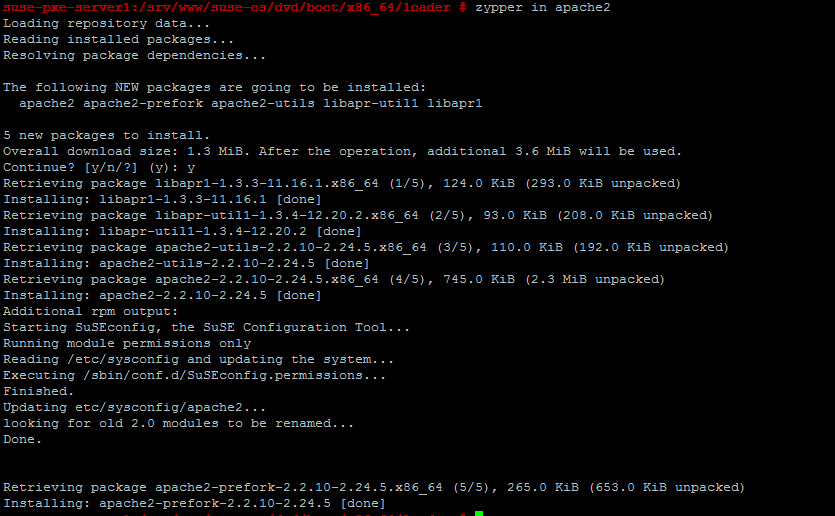
Step1 is finished. Now lets configure http to share the DVD image.install the apache2 package using the following command.
# zypper in apache2
Mount the SuSE Linux DVD into /srv/www/suse-os/dvd directory.
#mkdir -p /srv/www/suse-os/dvd
#mount /dev/sr0 /srv/www/suse-os/dvd
DVD is mounted, make the mount point persistent across reboot. add the following entry in /etc/fstab
/dev/sr0 /srv/www/suse-os/dvd iso9660 defaults 0 0
I am going to configure a virtual host in apache to provide the DVD image.
create a file named suse-os.conf under /etc/apache2/vhosts.d/ and add the following lines into suse-os.conf file.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin vinil@vinizlinux.com
ServerName pxe-suse.vinizlinux.com
DocumentRoot /srv/www/suse-os
<Directory "/srv/www/suse-os">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>

Start the apache using #rcapache2 start
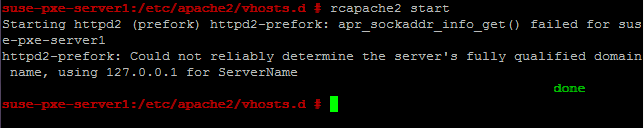
And enable the apache in startup using #chkconfig --level 35 apache2 on and then check the apache in a web browser.
Now the final part let us work on tftp part.
for configuring tftp we need to install the tftp package also we need the syslinux package which contains the pxelinux kernel to boot the client from PXE server.
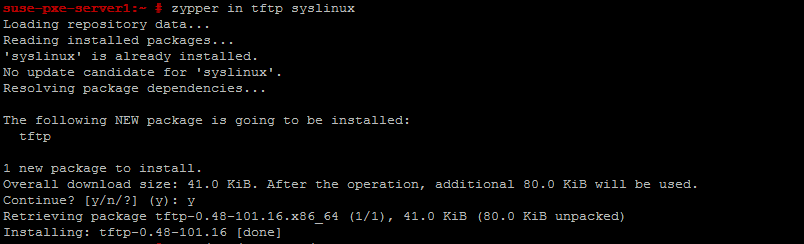
Run the following command to install tftp and syslinux package.
# zypper in tftp syslinux
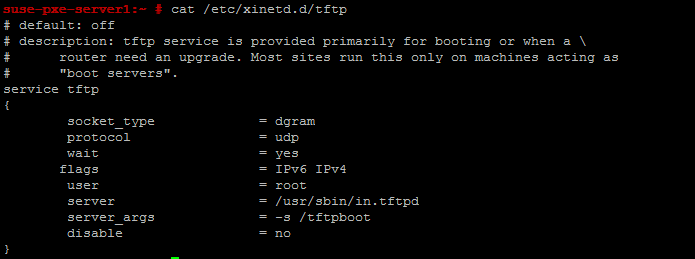
Edit the tftp configuration file /etc/xinetd.d/tftp and change the following line to "no".
disable = no

now copy the pxelinux.0 file to /tftpboot.
# cp /usr/share/syslinux/pxelinux.0 /tftpboot/
We need to copy some more supporting files for PXE boot for that we need to mount the SuSE OS DVD.
#mkdir -p /srv/www/suse-os/dvd
# mount /dev/sr0 /srv/www/suse-os/dvd
This same mount point can be used in Apache for giving the OS image to PXE clients. cd to /srv/www/suse-os/dvd/boot/x86_64/loader/ directory where we have the kernel , initrd, boot tests etc.
# cd /srv/www/suse-os/dvd/boot/x86_64/loader/
# cp linux initrd bootlogo memtest message biostest /tftpboot/
Copy the isolinux.cfg file to /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/ as default
# cp isolinux.cfg /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
Now edit the default file and provide the installation source and method of installation. here i am using ssh based suse installation. you could use vnc or ssh to do installation. Entries in the default file is shown below.
Now restart the xinetd services using the following command. and enable it on startup.
# rcxinetd start
#chkconfig --level 35 xinetd on
This installation is not fully automatic we need to give some inputs to complete the installation. for the automated installation we need to configure autoyast. i will put a new post on it later.
Now lets boot the client and check whether its able to boot or not.
Yes !! Yes!! its able to boot from PXE Server
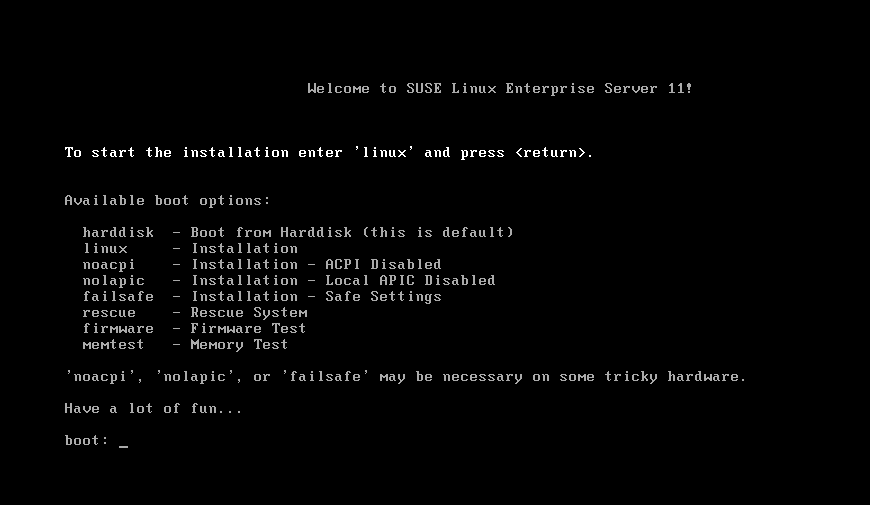
Now type linux on the prompt it will start installation.
After sometime you will see the following screen to start installation. you need to connect this client from anywhere using ssh to provide inputs for finishing the installation.
Here we are using ssh -X , and X is for X11/X.org forwarding.
Let us connect the client and check the installation.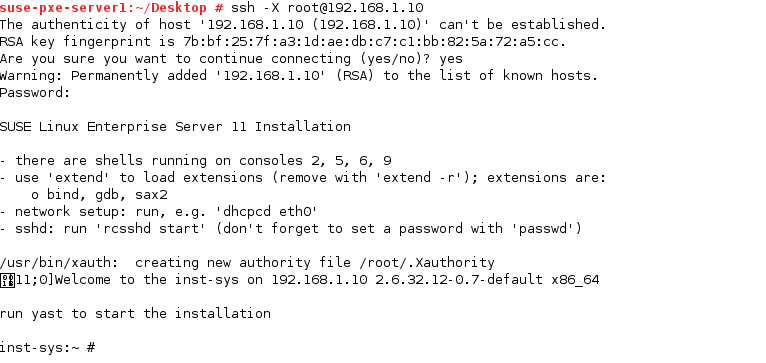
Now run yast on prompt it will open a GUI interface to start installation.
Follow the on-screen options and finish the installation.
That’s all! I will be coming up with few more interesting articles on Linux, till then stay tuned to Learn linux and don’t forget to add your valuable comments
Its been long time i did not put any contents in my blog. I was doing research in some interesting stuffs in linux and also busy with work. This time i am coming up with SuSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 not with Redhat. !
Let us discuss about how do we configure PXE server to install SuSE Linux Enterprise server OS into Clients. Similar post on RHEL 7 can be found on the following link : Complete Guide for PXE Server configuration in RHEL 7.0
Breaking down the task to configure PXE Server, Here is the list :
1. DHCP server ( To provide IP address to client )
2. Apache2 Server configuration ( To transfer the DVD image to Client for OS installation)
3. TFTP server configuration ( To Transfer the PXE kernel and other supporting files to Client System )
Check the version of SUSE Linux using the following command.

Let us configure DHCP Server first. for that we need to install the dhcp-server package into server.
I am using Zypper to install dhcp server pakage. or else you could run #yast dhcp-server to install and configure dhcp server.
# zypper in dhcp-server

Now configure dhcp server. edit the /etc/dhcpd.conf and update the following entries.
(Move original /etc/dhcpd.conf file to some other name and create new dhcpd.conf with the following entries.)
Here IP range is from 192.168.1.10 to 192.168.1.20
default-lease-time 14400;
ddns-update-style none;
subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range dynamic-bootp 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.20;
default-lease-time 14400;
max-lease-time 172800;
next-server 192.168.1.3;
filename "pxelinux.0";
}
update the /etc/sysconfig/dhcpd file with the following entries.
DHCPD_INTERFACE="eth0"
Restart the dhcpd service and enable it on start-up using the following command.
# rcdhcpd restart
#chkconfig --level 35 dhcpd on

Step1 is finished. Now lets configure http to share the DVD image.install the apache2 package using the following command.
# zypper in apache2

Mount the SuSE Linux DVD into /srv/www/suse-os/dvd directory.
#mkdir -p /srv/www/suse-os/dvd
#mount /dev/sr0 /srv/www/suse-os/dvd
DVD is mounted, make the mount point persistent across reboot. add the following entry in /etc/fstab
/dev/sr0 /srv/www/suse-os/dvd iso9660 defaults 0 0
create a file named suse-os.conf under /etc/apache2/vhosts.d/ and add the following lines into suse-os.conf file.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin vinil@vinizlinux.com
ServerName pxe-suse.vinizlinux.com
DocumentRoot /srv/www/suse-os
<Directory "/srv/www/suse-os">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>

Start the apache using #rcapache2 start

And enable the apache in startup using #chkconfig --level 35 apache2 on and then check the apache in a web browser.
Now the final part let us work on tftp part.
for configuring tftp we need to install the tftp package also we need the syslinux package which contains the pxelinux kernel to boot the client from PXE server.
Run the following command to install tftp and syslinux package.
# zypper in tftp syslinux

Edit the tftp configuration file /etc/xinetd.d/tftp and change the following line to "no".
disable = no

create the tftpboot directory under / and create the pxelinux.cfg directory under /tftpboot

now copy the pxelinux.0 file to /tftpboot.
# cp /usr/share/syslinux/pxelinux.0 /tftpboot/
We need to copy some more supporting files for PXE boot for that we need to mount the SuSE OS DVD.
#mkdir -p /srv/www/suse-os/dvd
# mount /dev/sr0 /srv/www/suse-os/dvd
This same mount point can be used in Apache for giving the OS image to PXE clients. cd to /srv/www/suse-os/dvd/boot/x86_64/loader/ directory where we have the kernel , initrd, boot tests etc.
# cd /srv/www/suse-os/dvd/boot/x86_64/loader/
# cp linux initrd bootlogo memtest message biostest /tftpboot/
Copy the isolinux.cfg file to /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/ as default
# cp isolinux.cfg /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
Now edit the default file and provide the installation source and method of installation. here i am using ssh based suse installation. you could use vnc or ssh to do installation. Entries in the default file is shown below.
Now restart the xinetd services using the following command. and enable it on startup.
# rcxinetd start
#chkconfig --level 35 xinetd on
This installation is not fully automatic we need to give some inputs to complete the installation. for the automated installation we need to configure autoyast. i will put a new post on it later.
Now lets boot the client and check whether its able to boot or not.
Yes !! Yes!! its able to boot from PXE Server

Now type linux on the prompt it will start installation.
After sometime you will see the following screen to start installation. you need to connect this client from anywhere using ssh to provide inputs for finishing the installation.
Here we are using ssh -X , and X is for X11/X.org forwarding.
Let us connect the client and check the installation.

Now run yast on prompt it will open a GUI interface to start installation.
Follow the on-screen options and finish the installation.
That’s all! I will be coming up with few more interesting articles on Linux, till then stay tuned to Learn linux and don’t forget to add your valuable comments






